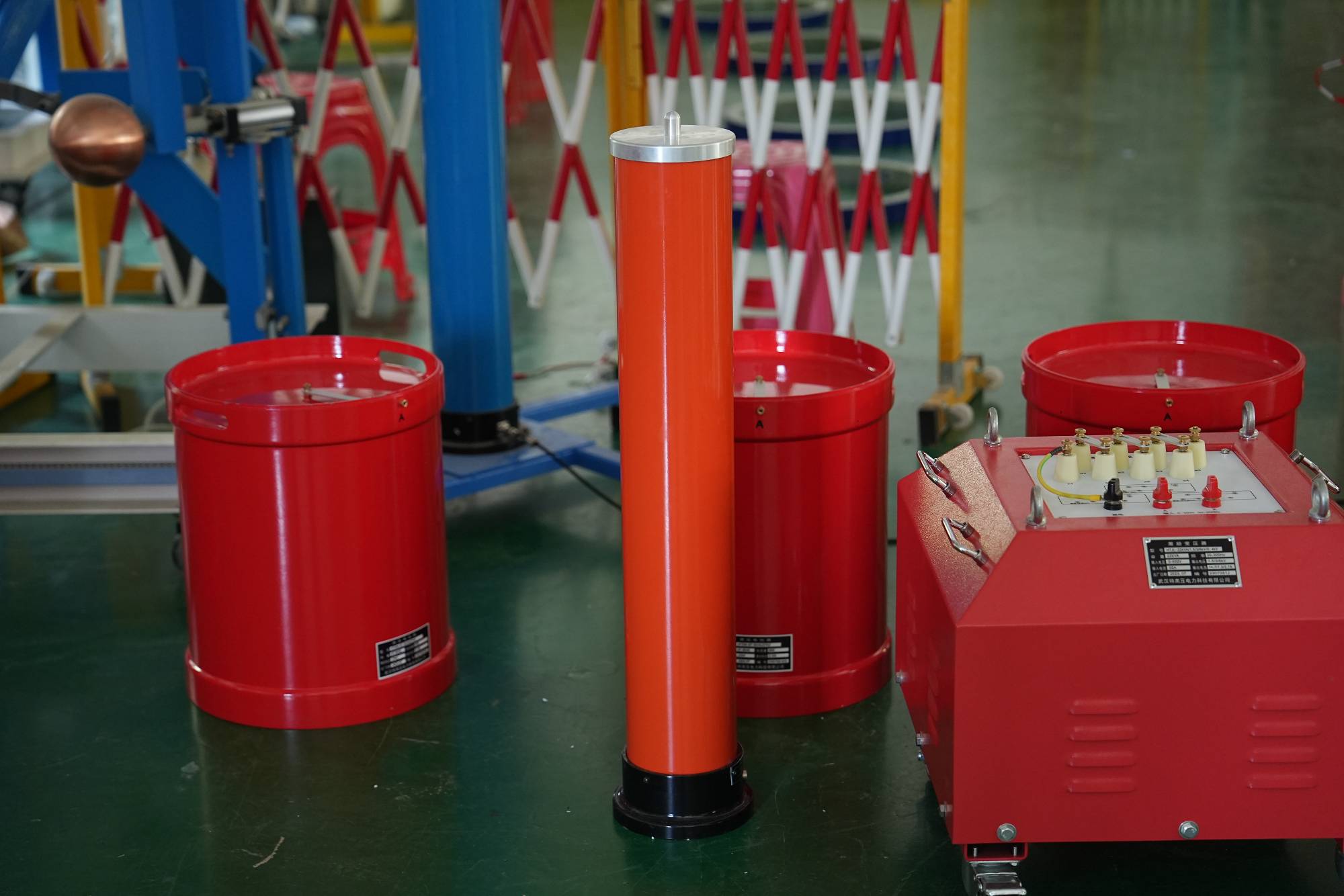
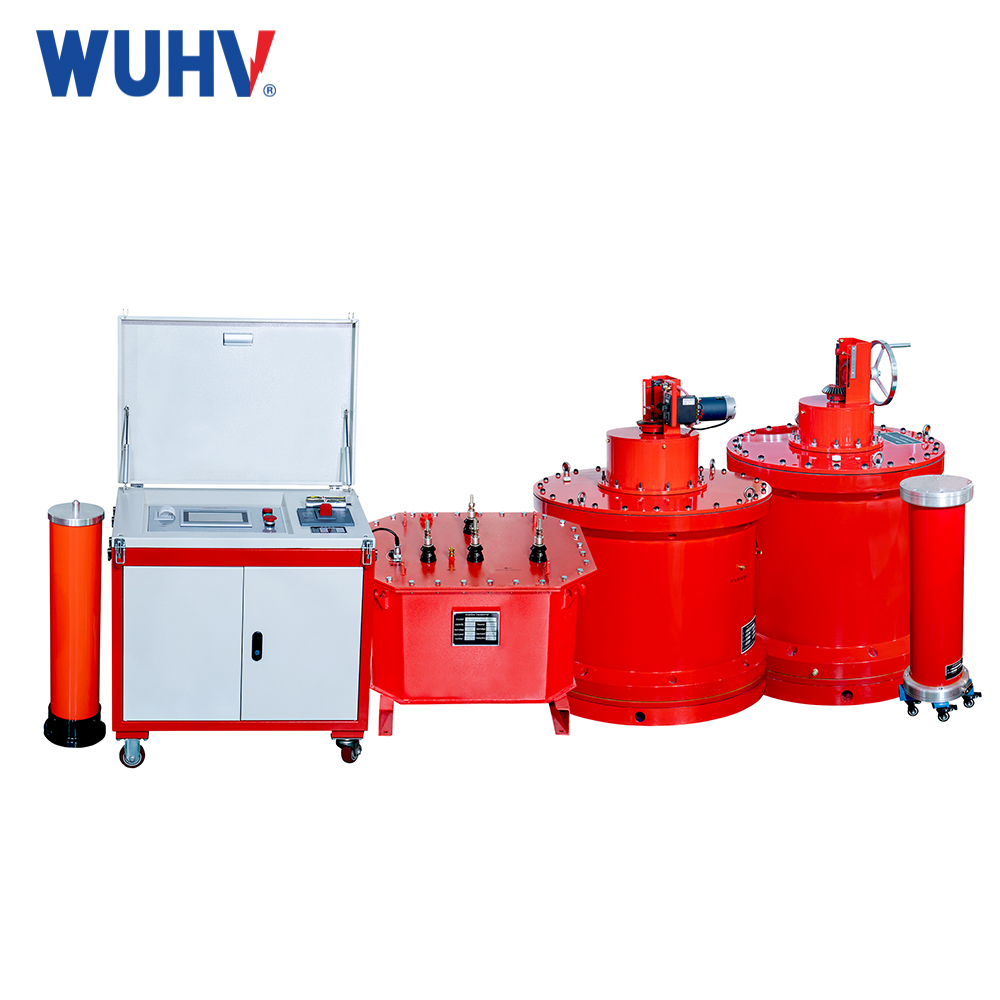
RLC series resonant circuit? Wuhan UHV specializes in producing RLC series resonant circuits, with a wide range of product options and professional electrical testing. When looking for RLC series resonant circuits, choose Wuhan UHV.
What is an RLC series circuit?
The series circuit composed of resistors, inductors, and capacitors is called an RLC series circuit.
What is circuit resonance?
A circuit composed of resistors, inductors, and capacitors, under the action of a sine power supply, exhibits resistive behavior when the voltage and current are in phase, and the working state of the circuit is called resonance.
At this point in the series circuit, the resonant circuit impedance | Z0 | is at its minimum, and the entire circuit is equivalent to a pure resistance circuit. The voltage of the excitation power supply is in phase with the response voltage of the circuit. During resonance, the inductance ω 0L is equal to the capacitive impedance 1/ω 0C, and the voltage UL on the inductance is equal to the voltage UC on the capacitor, with a phase difference of 180 °. When the excitation power supply voltage (effective value) remains constant, the current I=Ui/R in the resonant circuit is at its maximum value.
When 1- ω 2LC=O, | Au | reaches its maximum value; When ω is equal to a specific value ω 0, that is:
|When Au | reaches its maximum value of 1, at ω=ω 0, the output voltage is equal to the input voltage, and ω 0 is called the center frequency of the bandpass circuit. When | Au | drops to 70.7% of its maximum value, the two frequencies are the upper half power frequency and the lower half power frequency, with frequencies above the center frequency denoted as ω 2 and frequencies below the center frequency denoted as ω 1, as shown in the figure
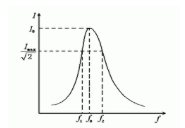
Resonance curve of RLC series circuit
Defined as passband BW, namely: rlc series resonant circuit.
Advantages of series resonance in power systems:
1. The required power capacity is greatly reduced. Series resonant power supply generates high voltage and high current through resonance between resonant reactor and the tested capacitor. In the entire system, the power supply only needs to provide the active consumption part of the system, so the required power supply for the test is only 1/Q of the test capacity.
2. The weight and volume of the equipment have been greatly reduced. In a series resonant power supply, not only is the bulky high-power voltage regulating device and ordinary high-power power frequency test transformer eliminated, but the resonant excitation power supply only requires 1/Q of the test capacity, greatly reducing the system weight and volume, usually 1/10-1/30 of ordinary test devices.
3. Improve the waveform of the output voltage. A resonant power supply is a resonant filtering circuit that can improve the waveform distortion of the output voltage, obtain a good sine waveform, and effectively prevent the accidental breakdown of the test sample by harmonic peaks.
4. Prevent large short-circuit currents from burning the fault point. In the series resonance state, when the weak point of the insulation of the test sample is broken down, the circuit immediately disengages and the loop current rapidly drops to 1/Q of the normal test current. However, when conducting voltage withstand tests in parallel resonance or test transformer mode, the breakdown current immediately increases by several tens of times. Compared with the two, the short-circuit current is hundreds of times different from the breakdown current. So series resonance can effectively identify insulation weaknesses without the concern of large short-circuit currents burning the fault point.
5. There will be no overvoltage recovery. When the test sample breaks down, due to the loss of resonance conditions, the high voltage immediately disappears, the arc immediately extinguishes, and the process of re establishing the recovery voltage is long. It is easy to disconnect the power supply before reaching the flashover voltage again. This voltage recovery process is an intermittent oscillation process of energy accumulation, which is long and does not result in any recovery overvoltage.




















